Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O decomposition at the U
decomposition at the U O
O surface in bicarbonate solution
surface in bicarbonate solutionMcGrady, J.; Kumagai, Yuta; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
RSC Advances (Internet), 11(46), p.28940 - 28948, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.83(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kokusen, Junya; Seki, Masakazu; Abe, Masayuki; Nakazaki, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Umeda, Miki; Kihara, Takehiro; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Tech 2005-004, 53 Pages, 2005/03
This report presents operating records of dissolution of uranium dioxide and concentration of uranyl nitrate solution and acid removal, which have been performed from 1994 through 2003, for the purpose of feeding 10% and 6% enriched uranyl nitrate solution fuel to Static Experimental Critical Facility(STACY) and Transient Experimental Critical Facility(TRACY) in Nuclear Fuel Safety Engineering Facility(NUCEF).
Haga, Takahisa*; Gunji, Kazuhiko; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sonoda, Takashi; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Sakai, Yutaka; Niitsuma, Yasushi; Togashi, Yoshihiro; Miyauchi, Masakatsu; Sato, Takeshi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2004-005, 54 Pages, 2004/02
Criticality experiments using uranyl nitrate solution fuel are being conducted at STACY (the Static Experiment Critical Facility) and TRACY (the Transient Experiment Critical Facility) in NUCEF (the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility). Chemical analyses of the solution have been carried out to take necessary data for criticality experiments, for treatment and control of the fuel, and for safeguards purpose at the analytical laboratory placed in NUCEF. About 300 samples are analyzed annually that provide various kinds of data, such as uranium concentration, isolation acid concentration, uranium isotopic composition, concentration of fission product (FP) nuclides, tri-butyl phosphoric acid (TBP) concentration, impurities in the solution fuel and so on. This report summarizes the analytical methods and quality management of the analysis for uranyl nitrate solution relating to the criticality experiments.
Mineo, Hideaki; Isogai, Hikaru; Morita, Yasuji; Uchiyama, Gunzo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(2), p.126 - 134, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)A simple equation was proposed for the dissolution rate of spent LWR fuel, of which the change in the dissolution area was estimated by taking into account of the area of the cracks occurring due to thermal shrinkage of the pellets during irradiation. The applicability of proposed equation was examined using LWR fuel dissolution test results in the present study as well as the results obtained by other workers. The equation showed good agreements with the dissolution test results obtained from spent fuel pellets and pulverized spent fuel. It was indicated that the proposed equation was simple and would be useful for the prediction of dissolution of spent LWR fuels. However, the initial effective dissolution area, the parameter of the equation, was found to depend on the temperature, which could not be explained by the proposed equation. Further studies on the role of other factors affecting dissolution rate, such as nitrous acid, in the dissolution of spent fuel was required.
Tonoike, Kotaro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Okubo, Kiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(4), p.238 - 245, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity effect of neutron interaction between two identical units containing low enriched (10%  enrichment) uranyl nitrate solution was measured in the STACY. The unit has 350mm of thickness and 690mm of width and distance between those two units was adjustable from 0mm to 1450mm. Condition of the solution was about 290gU/L in uranium concentration, about 0.8N in free nitric acid molarity, 24
enrichment) uranyl nitrate solution was measured in the STACY. The unit has 350mm of thickness and 690mm of width and distance between those two units was adjustable from 0mm to 1450mm. Condition of the solution was about 290gU/L in uranium concentration, about 0.8N in free nitric acid molarity, 24 27
27 C in temperature and about 1.4g/cm
C in temperature and about 1.4g/cm in solution density. The reactivity effect was estimated from variation of critical solution level from 495mm to 763mm depending on the core distance. The reactivity effect was also evaluated by the solid angle method and a computational method using the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP-4C and the nuclear data library JENDL3.2. Comparison of those estimations is presented.
in solution density. The reactivity effect was estimated from variation of critical solution level from 495mm to 763mm depending on the core distance. The reactivity effect was also evaluated by the solid angle method and a computational method using the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP-4C and the nuclear data library JENDL3.2. Comparison of those estimations is presented.
Mineo, Hideaki; Suzuki, Tadashi; Morita, Yasuji
Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environment Applications (Super Green 2003), p.334 - 338, 2003/00
Behavior of spent nuclear fuel in subcritical water was investigated to look at the feasibility of fission-products (FPs) separation without organic solvent. The study employed unirradiated UO particles simulating spent fuel burned up to 45,000MWdt
particles simulating spent fuel burned up to 45,000MWdt , which includes FP elements in oxide form: Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm. Also, alloy particles consisted of Mo, Ru, Rh and Pd were prepared to simulate the metallic phase of FP. 12.728 g of the fuel and 52 mg of the alloy were placed in a 10 ml pressure vessel, where subcritical water was fed. The temperature was 523, 573, 623 and 663K, while the pressure was kept at 29MPa. Dissolved fraction decreased with elevating temperature. It was found that more than 5% of Ba, Mo and Pr were respectively dissolved. The dissolved fraction of Sr and Rh were about 1%, and about 0.3% for Zr. La, Ce, Nd and Sm, indicated almost the same result as U, which was about 0.1%. It was suggested that the subcritical water could separate portion of FP. Further study would be carried out with smaller-sized fuel.
, which includes FP elements in oxide form: Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm. Also, alloy particles consisted of Mo, Ru, Rh and Pd were prepared to simulate the metallic phase of FP. 12.728 g of the fuel and 52 mg of the alloy were placed in a 10 ml pressure vessel, where subcritical water was fed. The temperature was 523, 573, 623 and 663K, while the pressure was kept at 29MPa. Dissolved fraction decreased with elevating temperature. It was found that more than 5% of Ba, Mo and Pr were respectively dissolved. The dissolved fraction of Sr and Rh were about 1%, and about 0.3% for Zr. La, Ce, Nd and Sm, indicated almost the same result as U, which was about 0.1%. It was suggested that the subcritical water could separate portion of FP. Further study would be carried out with smaller-sized fuel.
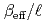 measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600
measurement on low enriched uranyl nitrate solution with single unit cores (600 , 280T, 800
, 280T, 800 ) of STACY
) of STACYTonoike, Kotaro; Miyoshi, Yoshinori; Kikuchi, Tsukasa*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(11), p.1227 - 1236, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kinetic parameter 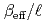 of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/
of low enriched uranyl nitrate solution was measured by the pulsed neutron source method in the STACY. This measurement was repeated systematically over several uranium concentrations from 193.7 gU/ to 432.1 gU/
to 432.1 gU/ . Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated
. Used core tanks were two cylindrical tanks whose diameters are 600 mm and 800 mm and one slab tank which has 280 mm thickness and 700 mm width. In this report, experimental data such as solution conditions, critical solution level for each solution condition, subcritical solution levels where measurements were conducted, measured decay time constants of prompt neutron and extrapolated 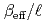 values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method.
values are described as well as basic principle of the pulsed neutron source method. 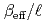 values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational
values were evaluated also by computation with the diffusion code CITATION in SRAC and the nuclear data library JENDL 3.2. Both experimental and computational 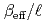 values show good agreement.
values show good agreement.
Nakajima, Ken
Proceedings of International Conference on the New Frontiers of Nuclear Technology; Reactor Physics, Safety and High-Performance Computing (PHYSOR 2002) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2002/10
The nuclear characteristics of TRACY, such as the criticality, the 
 /
/ ratio, the peak power, the energy of pulse, and the total energy, have been evaluated using the experimental data. TRACY is a supercritical reactor fueled with low-enriched uranyl nitrate aqueous solution to simulate criticality accidents in a fuel processing facility, such as a spent-fuel reprocessing plant. In this evaluation, the availability of criticality calculation and the models to evaluate the power and energy have been studied.
ratio, the peak power, the energy of pulse, and the total energy, have been evaluated using the experimental data. TRACY is a supercritical reactor fueled with low-enriched uranyl nitrate aqueous solution to simulate criticality accidents in a fuel processing facility, such as a spent-fuel reprocessing plant. In this evaluation, the availability of criticality calculation and the models to evaluate the power and energy have been studied.
Sakurai, Satoshi; Tachimori, Shoichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(2), p.187 - 189, 1996/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:82.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -U
-U N
N
Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Fukuda, Kosaku; *
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 232, p.274 - 280, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:50.6(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Ken; ; ; ; *; Sakuraba, Koichi; Ono, Akio
PHYSOR 96: Int. Conf. on the Physics of Reactors, 4, p.L83 - L92, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Komiyama, Kazumasa*; Okuno, Hiroshi
JAERI-Research 94-047, 39 Pages, 1994/12
no abstracts in English
 and
and  (
( ) counting using a CsI(T1) scintillator
) counting using a CsI(T1) scintillatorUsuda, Shigekazu; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 321, p.242 - 246, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:81.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Takaumi; J.G.Serrano*; ; *; Takeishi, Hideyo
Radiochimica Acta, 58-59, p.173 - 178, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
; Arai, Yasuo; Iwai, Takashi; Omichi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(7), p.689 - 691, 1991/07
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Takeshita, Isao; Nomura, Masayuki; ; Tsujino, Takeshi
Proc. of the CSNI Specialist Meeting on Safety and Risk Assessment in Fuel Cycle Facilities, p.461 - 470, 1991/00
no abstracts in English

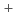
 solid solutions
solid solutionsUgajin, Mitsuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 110, p.140 - 146, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:88.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; ;
Anal. Chem., 52(11), p.1601 - 1606, 1980/00
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:37.58(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
; ;
Fresenius'Z.Anal.Chem., 303(1), P. 28, 1980/00
no abstracts in English
; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10(2), p.95 - 100, 1973/02
no abstracts in English